The LanDS ML procedure combines available global and regional datasets with site specific characteristics, leveraging on the knowledge and expertise coming from REACT4MED Ecosystem Restoration Living Labs (ERLLs), to classify different areas in terms of climatic trends and socio-economic circumstances, land degradation severity and applicability for the restoration measures considered in the project. The ML tool can be sourced with historical and future climate and socio-economic scenarios, based on bio-physical, climate and socioeconomic variables (computed from WP2 data), to support better-informed land restoration actions and impact assessment (WP5) and to provide useful insights for policy recommendations and support decision-making processes (WP6).
The different spatial and temporal resolutions and time horizons of the original datasets (see Section 2 of D2.4 Past and Future Drivers of Change) led to a necessary compromise to create a consistent input dataset for the ML procedure, which is consequently characterised as follows:
- Temporal coverage: 2001 – 2019, the only time horizon common for all data;
- Temporal resolution: all indicators have been computed at a yearly time step and later aggregated over the time horizon or every five years, depending on the configuration run;
- Spatial extent: Mediterranean region, defined by the hydrological basins draining towards the Mediterranean Sea from Hydrobasins 05 level (Lehner and Grill, 2013), as used also in the specific climate classifications for the Mediterranean (Allam et al., 2020) and adding the subbasins belonging to Merchouch (MO) and Tamia (EG), to include REACT4MED Pilot Areas in Morocco and Egypt, respectively;
- Spatial resolution: 0.125 x 0.125 degrees.
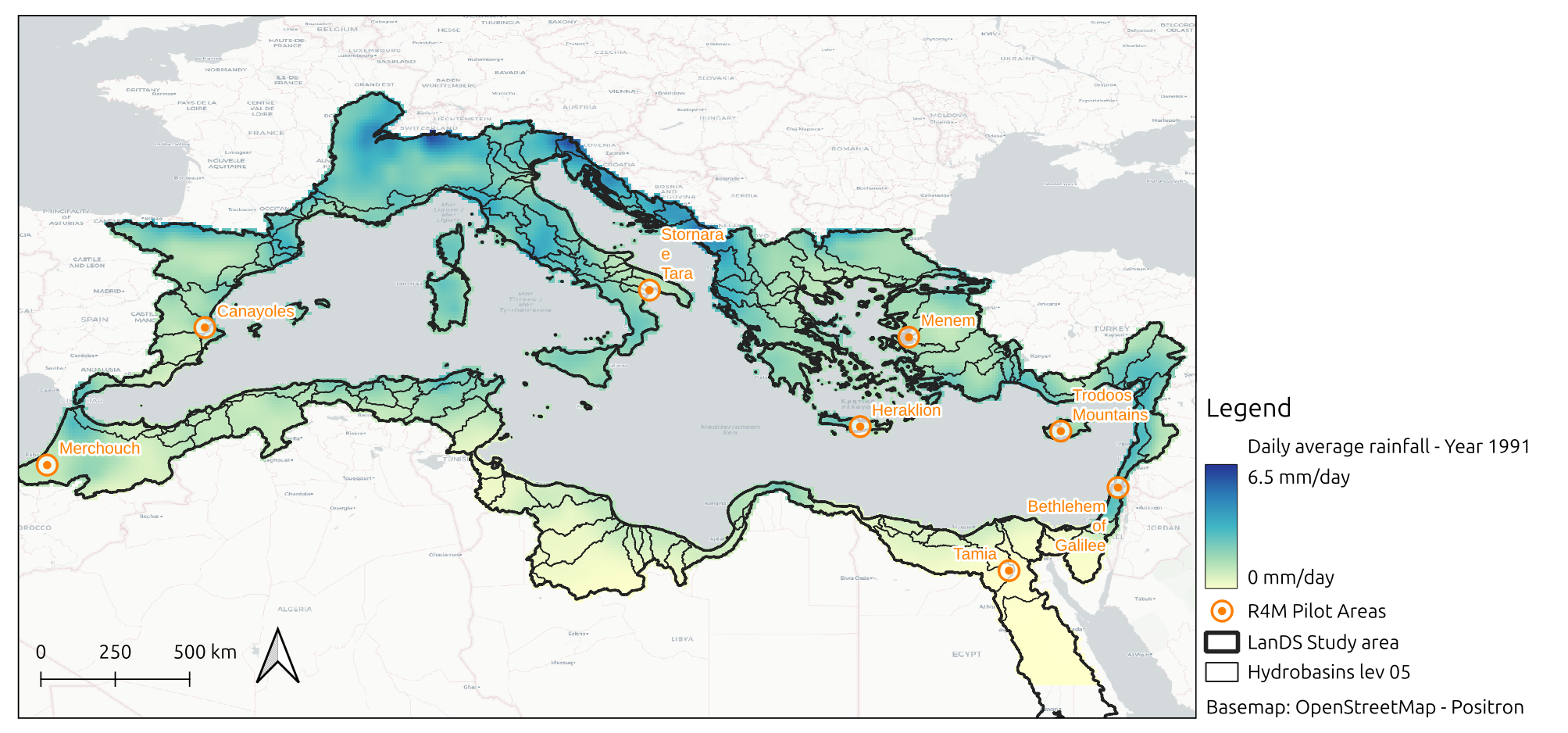
An example of input is shown in the figure above, displaying the Precipitation Average Index (PrAvg) for year 1991, at the spatial extent considered for the ML tool.
The LanDS ML procedure for the identification of potentially suitable areas in the Mediterranean to up- and outscale REACT4MED restoration actions can be summarised in the following working steps:
- The candidate ML tool inputs are computed for a reference past period, using the LanDS-computed indicators based on Task 2.4 datasets (for more details, see D2.4 Past and Future Drivers of Change);
- Input Variable Selection (IVS) is run checking the candidate inputs relevance and redundancy by a correlation analysis and a Principal Component Analysis (PCA), to eventually reduce the inputs set to the most significant ones;
- A clustering analysis (k-means) based on the inputs set obtained in step 2 is run to find areas with similar characteristics in the Mediterranean region.
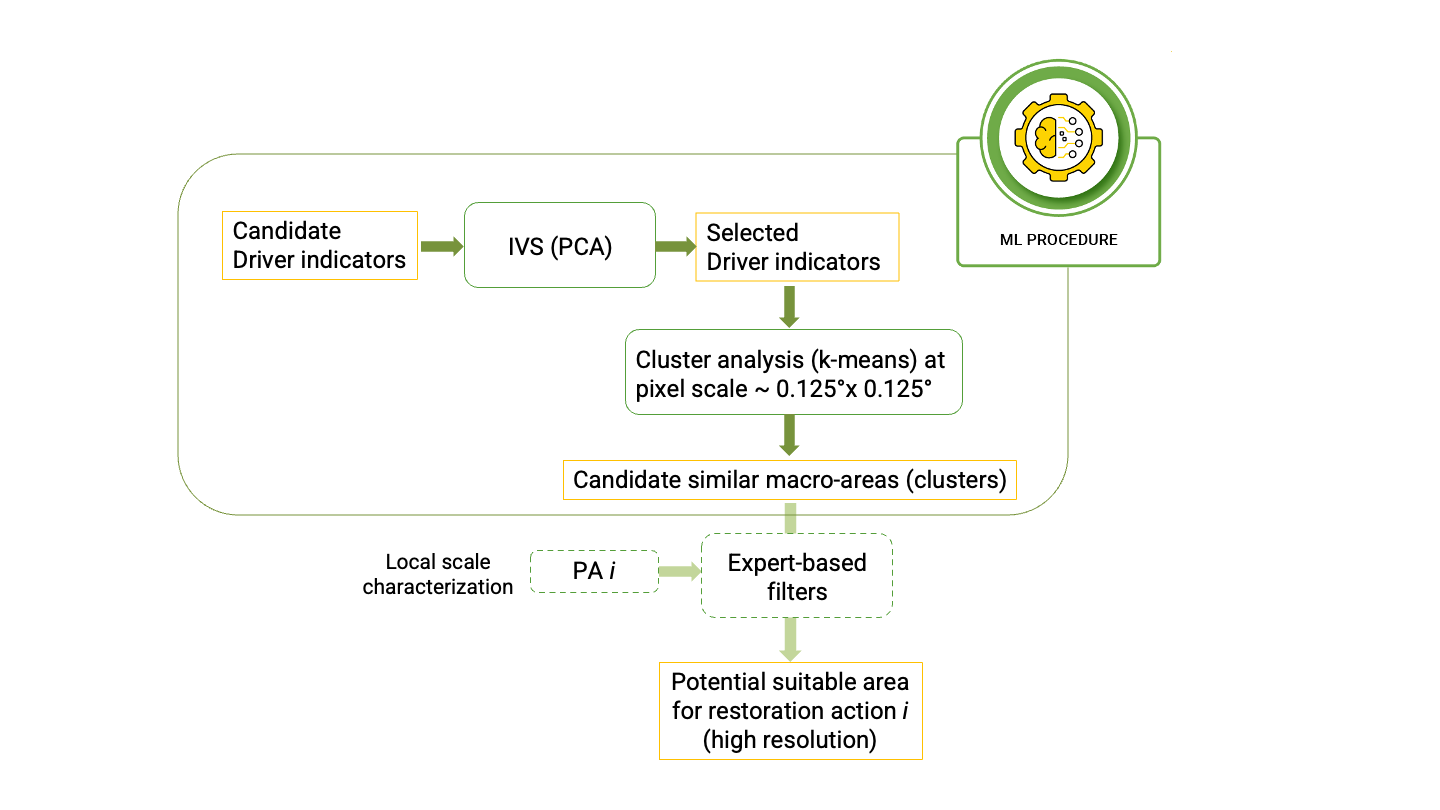
The outcomes of step 3 will serve the expert-based analysis integrating higher resolution datasets and specific local conditions to find potentially suitable areas for each specific project restoration action.
The software code has been released on the LanDS Gitlab repository and can be used to run step 2 and 3 of the procedure.
For more details, please refer to Deliverable D4.3 LanDS Toolbox.